Smart Pointer
在C++11中通过引入智能指针的概念,使得C++程序员不需要手动释放内存
智能指针的种类
- std::unique_ptr
- std::shared_ptr
- std::weak_ptr
概述
C++的指针包括两种
智能指针是原始指针的封装,其优点是会自动分配内存,不用担心潜在的内存泄露。
unique_ptr
在任何给定的时刻,只能有一个指针管理内存
当指针超出作用域时,内存将自动释放
该类型指针不可Copy,只能Move
创建方式
通过已有裸指针创建
1
2
3
4
5
| Cat *c_p2 = new Cat("p2");
std::unique_ptr<Cat> u_c_p2{c_p2};
c_p2 = nullptr;
u_c_p2->cat_info();
|
通过new来创建
1
2
3
4
| std::unique_ptr<Cat> u_c_p3{new Cat("dd")};
u_c_p3->cat_info();
u_c_p3->set_cat_name("oo");
u_c_p3->cat_info();
|
通过std::make_unique创建
1
2
3
4
| std::unique_ptr<Cat> u_c_p4 = std::make_unique<Cat>();
u_c_p4->cat_info();
u_c_p4->set_cat_name("oo");
u_c_p4->cat_info();
|
通过get()获取地址
函数调用
值传递
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| void do_with_cat_pass_value(std::unique_ptr<Cat> c) {
c->cat_info();
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
std::unique_ptr<Cat> c1 = std::make_unique<Cat>("ff");
do_with_cat_pass_value(c1);
}
|
报错
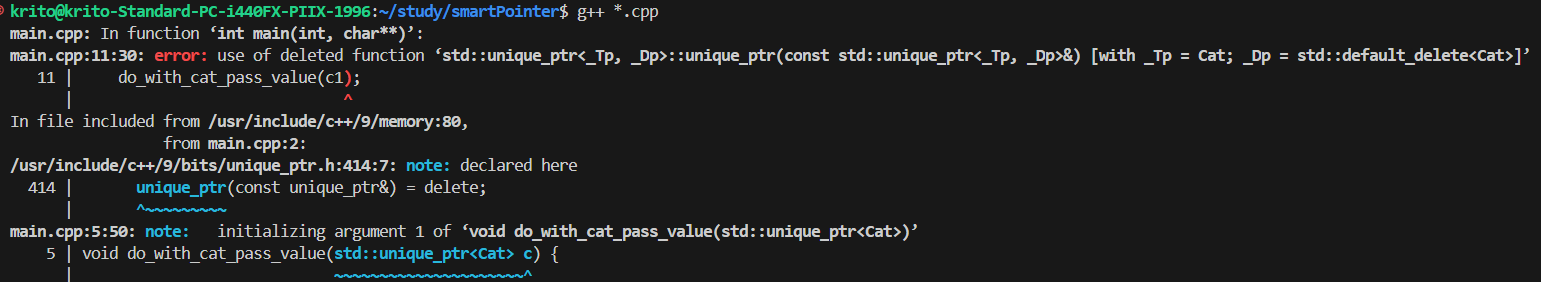
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| void do_with_cat_pass_value(std::unique_ptr<Cat> c) {
c->cat_info();
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
std::unique_ptr<Cat> c1 = std::make_unique<Cat>("ff");
do_with_cat_pass_value(move(c1));
}
|
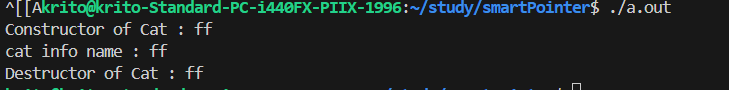
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| void do_with_cat_pass_value(std::unique_ptr<Cat> c) {
c->cat_info();
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
std::unique_ptr<Cat> c1 = std::make_unique<Cat>("ff");
do_with_cat_pass_value(move(c1));
c1->cat_info();
}
|
报错,move将c1指向的资源转移。
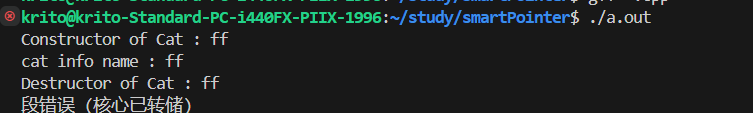
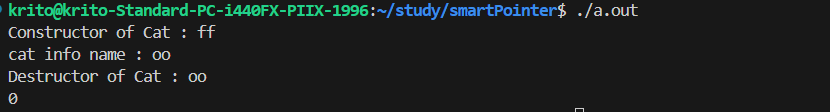
引用传递
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| void do_with_cat_pass_ref(std::unique_ptr<Cat> &c) {
c->set_cat_name("oo");
c->cat_info();
c.reset();
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
std::unique_ptr<Cat> c1 = std::make_unique<Cat>("ff");
do_with_cat_pass_ref(c1);
std::cout << c1.get() << std::endl;
}
|
shared_ptr
shared_ptr 计数指针又称共享指针,与unique_ptr不同的时它可以共享数据。
shared_ptr 创建了一个计数器与类对象所指的内存相关联,Copy则计数器加一,销毁则计数器减一。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
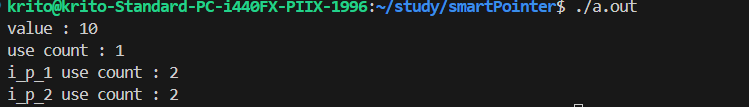
| int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
std::shared_ptr<int> i_p_1 = std::make_shared<int>(10);
std::cout << "value : " << *i_p_1 << std::endl;
std::cout << "use count : "<< i_p_1.use_count() << std::endl;
std::shared_ptr<int> i_p_2 = i_p_1;
std::cout << "i_p_1 use count : " << i_p_1.use_count() << std::endl;
std::cout << "i_p_2 use count : " << i_p_2.use_count() << std::endl;
}
|
shared_ptr与unique_ptr
不能将shared_ptr转换为unique_ptr。
unique_ptr可以转换为shared_ptr,通过std::move。
函数返回值推荐使用unique_ptr,因为可以根据需要随时转换为shared_ptr。
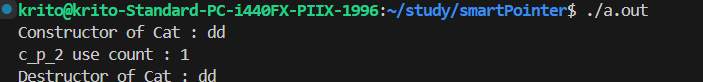
1
2
3
4
5
| int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
std::unique_ptr<Cat> c_p_1 = std::make_unique<Cat>("dd");
std::shared_ptr<Cat> c_p_2 = std::move(c_p_1);
std::cout << "c_p_2 use count : " << c_p_2.use_count() << std::endl;
}
|
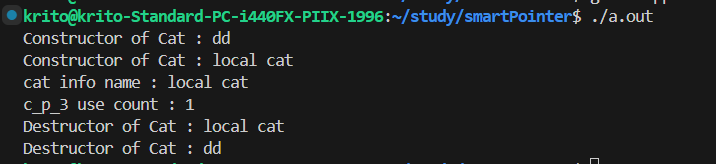
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| std::unique_ptr<Cat> get_unqiue_ptr() {
std::unique_ptr<Cat> p = std::make_unique<Cat>("local cat");
return p;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
std::unique_ptr<Cat> c_p_1 = std::make_unique<Cat>("dd");
std::shared_ptr<Cat> c_p_2 = std::move(c_p_1);
std::shared_ptr<Cat> c_p_3 = get_unqiue_ptr();
if(c_p_3) {
c_p_3->cat_info();
std::cout << "c_p_3 use count : " << c_p_3.use_count() << std::endl;
}
}
|
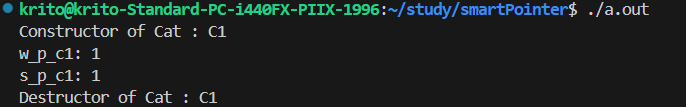
weak_ptr
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
std::shared_ptr<Cat> s_p_c1 = std::make_shared<Cat>("C1");
std::weak_ptr<Cat> w_p_c1{s_p_c1};
std::cout << "w_p_c1: " << w_p_c1.use_count() << std::endl;
std::cout << "s_p_c1: " << s_p_c1.use_count() << std::endl;
}
|
weak_ptr的创建不会使得计数器增加
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
std::shared_ptr<Cat> s_p_c1 = std::make_shared<Cat>("C1");
std::weak_ptr<Cat> w_p_c1{s_p_c1};
std::cout << "w_p_c1: " << w_p_c1.use_count() << std::endl;
std::cout << "s_p_c1: " << s_p_c1.use_count() << std::endl;
std::shared_ptr<Cat> s_p_c2 = w_p_c1.lock();
std::cout << "w_p_c1: " << w_p_c1.use_count() << std::endl;
std::cout << "s_p_c1: " << s_p_c1.use_count() << std::endl;
std::cout << "s_p_c2: " << s_p_c2.use_count() << std::endl;
}
|
可以通过lock,将类型转换为shared_ptr。
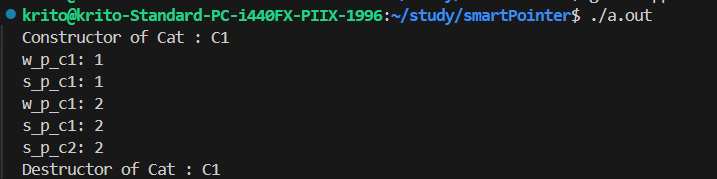
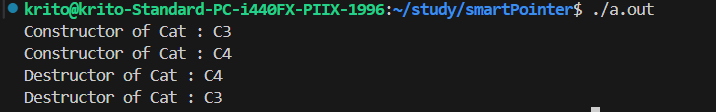
正常情况下c3,c4都会被销毁
1
2
| std::shared_ptr<Cat> c3 = std::make_shared<Cat>("C3");
std::shared_ptr<Cat> c4 = std::make_shared<Cat>("C4");
|
1
2
3
4
| std::shared_ptr<Cat> c3 = std::make_shared<Cat>("C3");
std::shared_ptr<Cat> c4 = std::make_shared<Cat>("C4");
c3->set_friend(c4);
c4->set_friend(c3);
|
无法正常销毁,存在循环依赖问题。
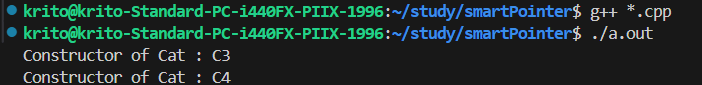
1
2
3
| private:
std::string name{"Mimi"};
std::shared_ptr<Cat> m_friend;
|
将shard_ptr更换成weak_ptr即可正常销毁。
weak_ptr可以解决资源销毁时的循环依赖问题。
粗糙的代码实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
| #include <iostream>
#include "cat.h"
class share_count {
public:
share_count() : _count(1) {}
void add_count() {
++_count;
}
long reduce_count() {
return --_count;
}
long get_count() const {
return _count;
}
private:
long _count;
};
template<typename T>
class smart_ptr
{
public:
smart_ptr(T* ptr = NULL) : m_ptr(ptr) {
if (ptr) {
m_share_count = new share_count;
}
}
~smart_ptr() {
if (m_ptr && !m_share_count->reduce_count()) {
delete m_ptr;
delete m_share_count;
std::cout << "~smart_ptr" << std::endl;
}
}
T& operator*() const {return *m_ptr;}
T* operator->() const {return m_ptr;}
operator bool() const {return m_ptr;}
smart_ptr(const smart_ptr& rhs) noexcept {
m_ptr = rhs.m_ptr;
m_share_count = rhs.m_share_count;
m_share_count->add_count();
}
smart_ptr& operator=(const smart_ptr& rhs) noexcept {
m_ptr = rhs.m_ptr;
m_share_count = rhs.m_share_count;
m_share_count->add_count();
return *this;
}
long use_count() const {
if (m_ptr) {
return m_share_count->get_count();
}
return 0;
}
private:
T* m_ptr;
share_count* m_share_count;
};
int main() {
smart_ptr<Cat> sp1{new Cat("S")};
std::cout << "sp1 user count : " << sp1.use_count() << std::endl;
smart_ptr<Cat> sp2{sp1};
std::cout << "sp2 user cout : " << sp2.use_count() << std::endl;
std::cout << "sp1 user cout : " << sp1.use_count() << std::endl;
smart_ptr<Cat> sp3;
sp3 = sp2;
std::cout << "sp3 user cout : " << sp3.use_count() << std::endl;
std::cout << "sp2 user cout : " << sp2.use_count() << std::endl;
std::cout << "sp1 user cout : " << sp1.use_count() << std::endl;
}
|










